What Is Open Data?
Open data are different in the way that any interested user may easily get free access to these data, freely use them and share them with others.
Open government data stands for a policy whose aim is to make government institutions’ activities and accountability more transparent to the population. Governments around the world are making attempts to render their data available, which will be favorable for positive social and economic reformation. This tendency can be observed not only in countries with developed economy. An increasing number of developing countries in Asia, Africa and Latin America adopt open data policies and publish data which used to be intended for internal use only. By placing their data in the public domain governments increase trust of citizens and contribute to businesses and education. Publishing open government data is a global trend of providing all interested users with access to these data to facilitate decision-making in various industries.
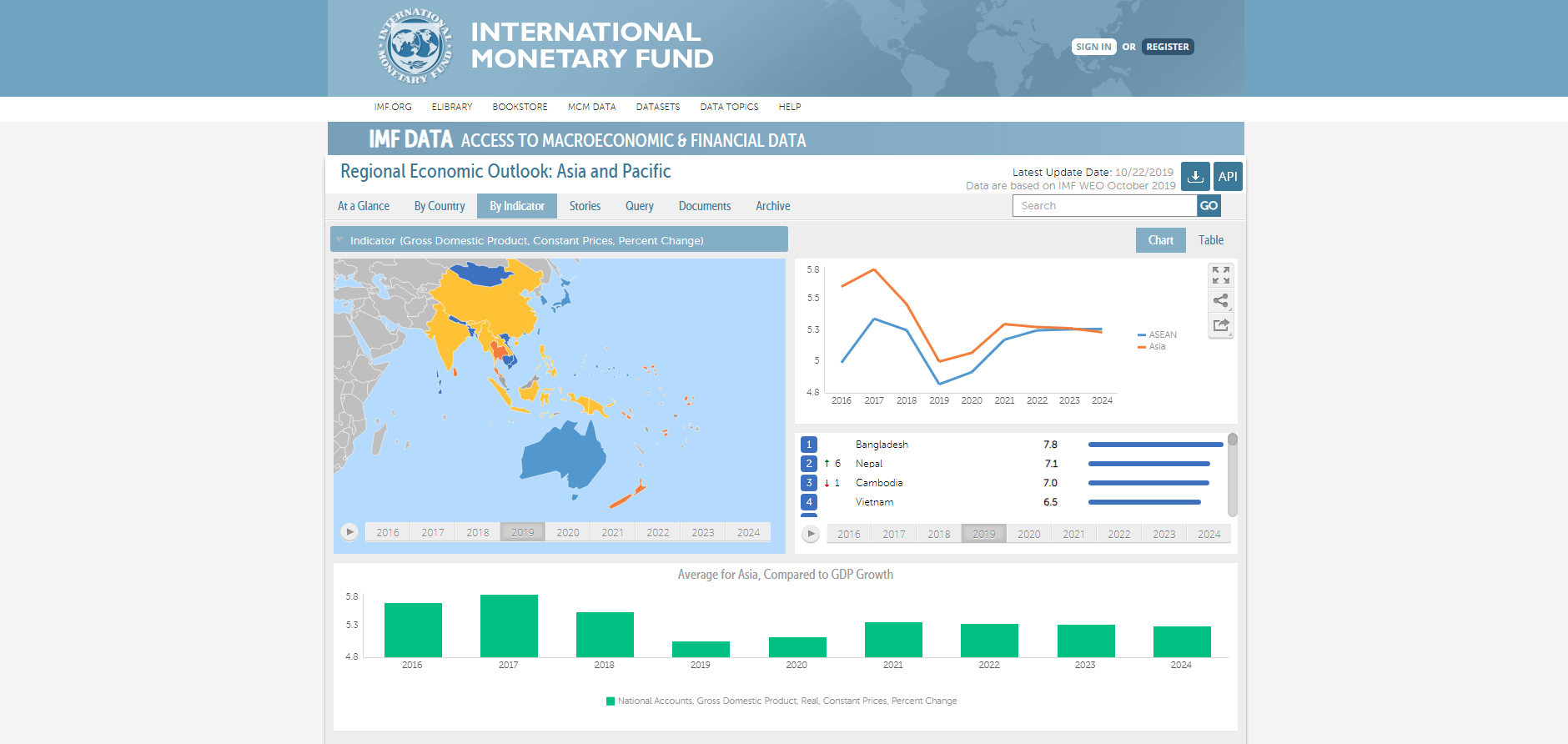
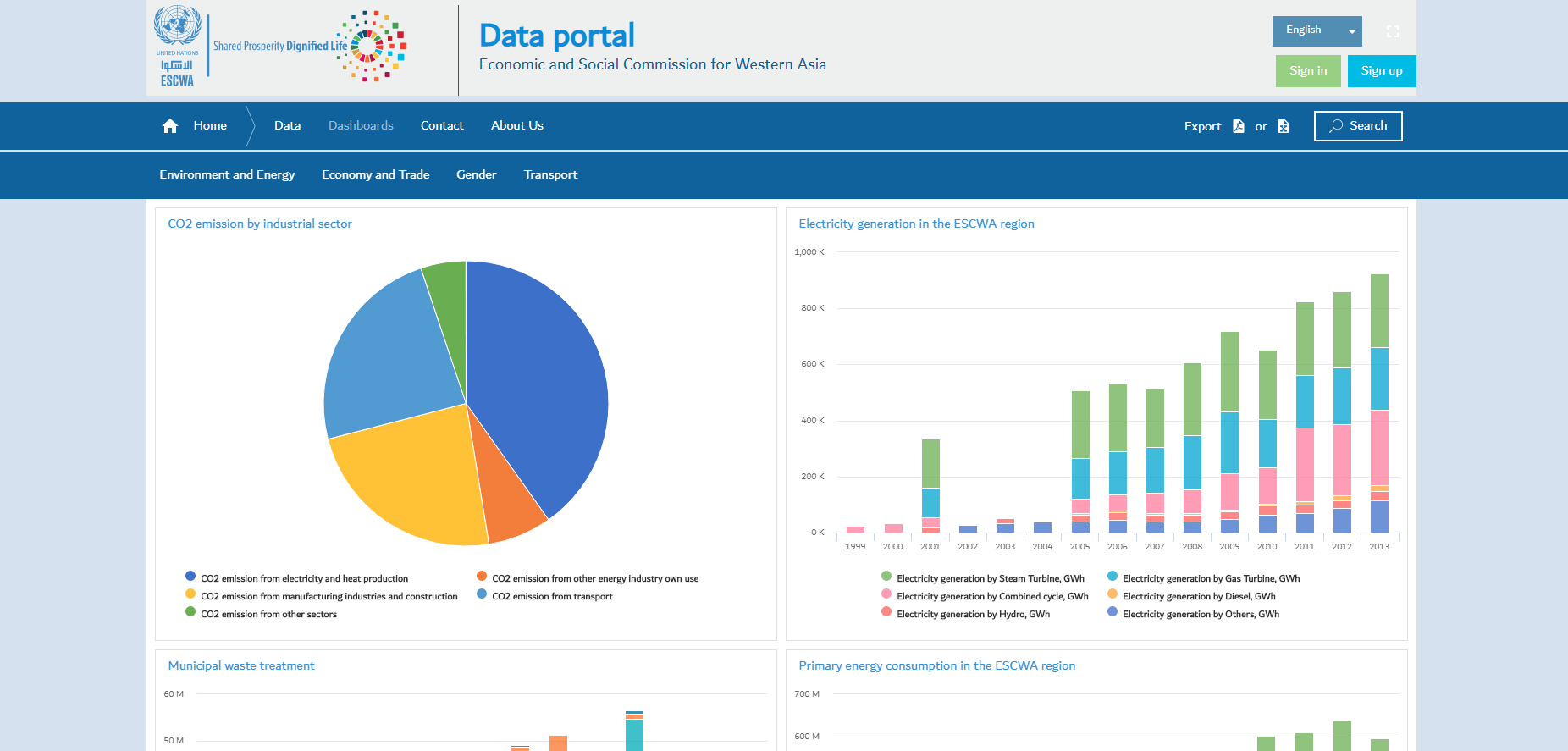
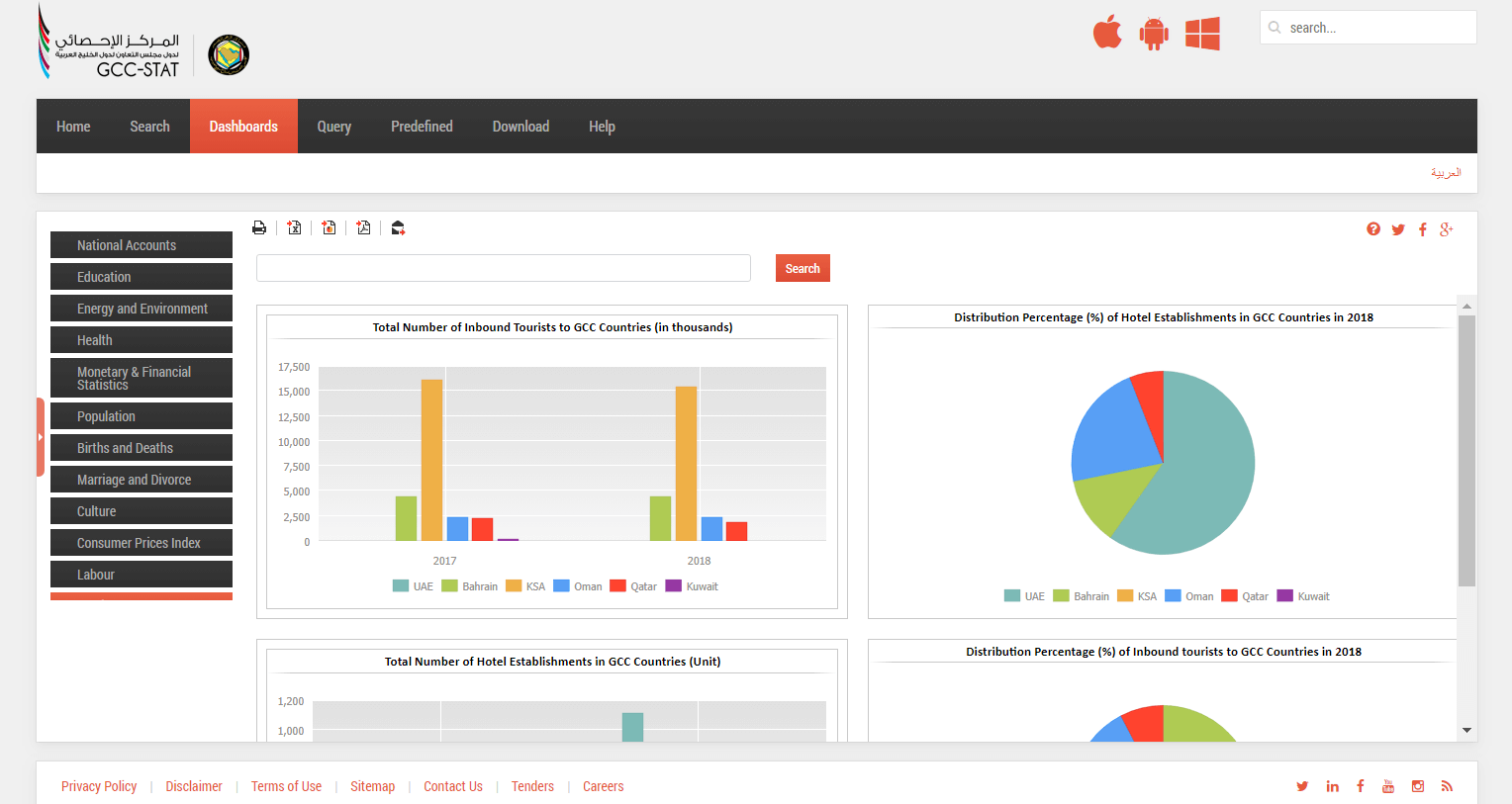
There are several examples below of open data portals in different fields – economy, demography, education and others. Developed by specialists at Smart Analytics, they enable any user to browse, analyse, download and share any information of interest.